A 1906 edition of the Original Stories from Real Life; with Conversations, calculated to Regulate the Affections and Form the Mind to Truth and Goodness. Reprinted from the 1791 edition, which contains 5 illustrations by William Blake.
About the book (from Wikipedia):
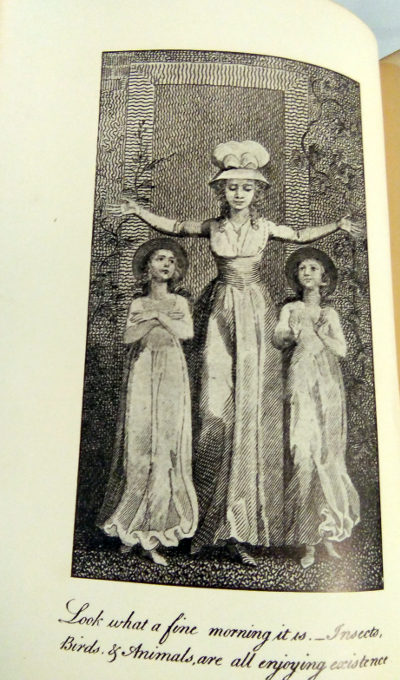
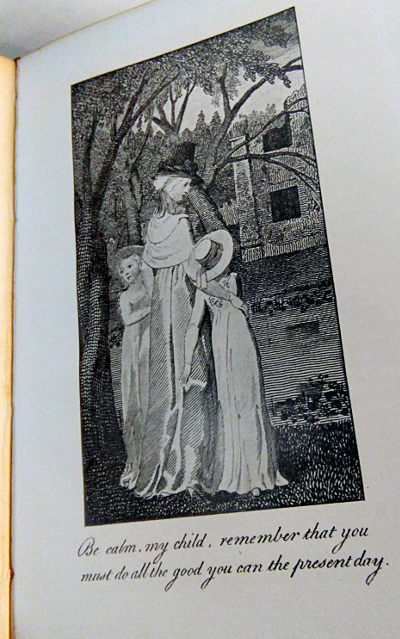
Original Stories from Real Life; with Conversations Calculated to Regulate the Affections, and Form the Mind to Truth and Goodness is the only complete work of children’s literature by the 18th-century English feminist author Mary Wollstonecraft. Original Stories begins with a frame story that sketches out the education of two young girls by their maternal teacher Mrs. Mason, followed by a series of didactic tales. The book was first published by Joseph Johnson in 1788; a second, illustrated edition, with engravings by William Blake, was released in 1791 and remained in print for around a quarter of a century.
In Original Stories, Wollstonecraft employed the then-burgeoning genre of children’s literature to promote the education of women and an emerging middle-class ideology. She argued that women would be able to become rational adults if they were educated properly as children, which was not a widely held belief in the 18th century, and contended that the nascent middle-class ethos was superior to the court culture represented by fairy tales and to the values of chance and luck found in chapbook stories for the poor. Wollstonecraft, in developing her own pedagogy, also responded to the works of the two most important educational theorists of the 18th century: John Locke and Jean-Jacques Rousseau.
About Mary Wollstonecraft (from Wikipedia):
Mary Wollstonecraft (27 April 1759 – 10 September 1797) was an English writer, philosopher, and advocate of women’s rights. During her brief career, she wrote novels, treatises, a travel narrative, a history of the French Revolution, a conduct book, and a children’s book. Wollstonecraft is best known for A Vindication of the Rights of Woman (1792), in which she argues that women are not naturally inferior to men, but appear to be only because they lack education. She suggests that both men and women should be treated as rational beings and imagines a social order founded on reason.