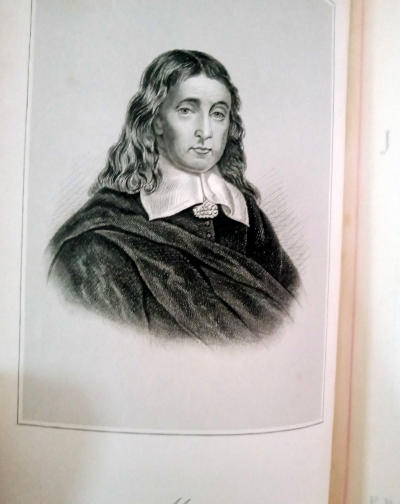
John Milton (9 December 1608 – 8 November 1674) was an English poet, polemicist, a scholarly man of letters, and a civil servant for the Commonwealth of England under Oliver Cromwell. He wrote at a time of religious flux and political upheaval, and is best known for his epic poem Paradise Lost.
Milton’s poetry and prose reflect deep personal convictions, a passion for freedom and self-determination, and the urgent issues and political turbulence of his day. Writing in English, Latin, and Italian, he achieved international renown within his lifetime, and his celebrated Areopagitica, (written in condemnation of pre-publication censorship) is among history’s most influential and impassioned defenses of free speech and freedom of the press.
William Hayley’s 1796 biography called him the “greatest English author,” and he remains generally regarded “as one of the preeminent writers in the English language”.
Paradise Lost
Paradise Lost is an epic poem in blank verse by the 17th-century English poet John Milton. It was originally published in 1667 in ten books, with a total of over ten thousand individual lines of verse. A second edition followed in 1674, redivided into twelve books with minor revisions throughout and a note on the versification; the majority of the poem was written while Milton was blind, and was transcribed for him.
The poem concerns the Christian story of the Fall of Man: the temptation of Adam and Eve by the fallen angel Satan and their expulsion from the Garden of Eden. Milton’s purpose, stated in Book I, is to “justify the ways of God to men” and elucidate the conflict between God’s eternal foresight and free will.
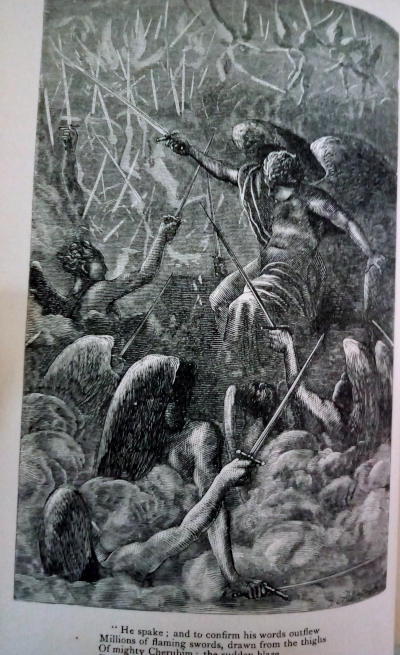
Milton incorporates Paganism, classical Greek references, and Christianity within the poem. It deals with diverse topics from marriage, politics and monarchy, and grapples with many difficult theological issues, including fate, predestination, the Trinity, and the introduction of sin and death into the world, as well as angels, fallen angels, Satan, and the war in heaven. Milton draws on his knowledge of languages, and diverse sources – primarily Genesis, much of the New Testament, the deuterocanonical Book of Enoch, and other parts of the Old Testament. Milton’s epic is generally considered one of the greatest literary works in the English language.
Paradise Regained
Paradise Regained deals with the subject of the Temptation of Christ.
The poem was composed in Milton’s cottage in Chalfont St Giles in Buckinghamshire, and was based on the Gospel of Luke’s version of the Temptation of Christ. Paradise Regained is four books in length, in contrast with Paradise Lost’s twelve.
One of the major concepts emphasized throughout Paradise Regained is the play on reversals. As implied by its title, Milton sets out to reverse the “loss” of Paradise. Thus, antonyms are often found next to each other throughout the poem, reinforcing the idea that everything that was lost in the first epic is going to be regained by the end of the mini-epic.
Additionally, this work focuses on the idea of “hunger”, both in a literal and in a spiritual sense. After wandering in the wilderness for forty days Jesus is starved of both food and the Word of God. Satan, too blind to see any non-literal meanings of the term, offers Christ food and various other temptations, but Jesus continually denies him.